Infrastructure technologies
Smart maintenance and management of social infrastructure
Achieve "smart world" with telecommunications platforms/facilities and other civil infrastructure solutions.
Action
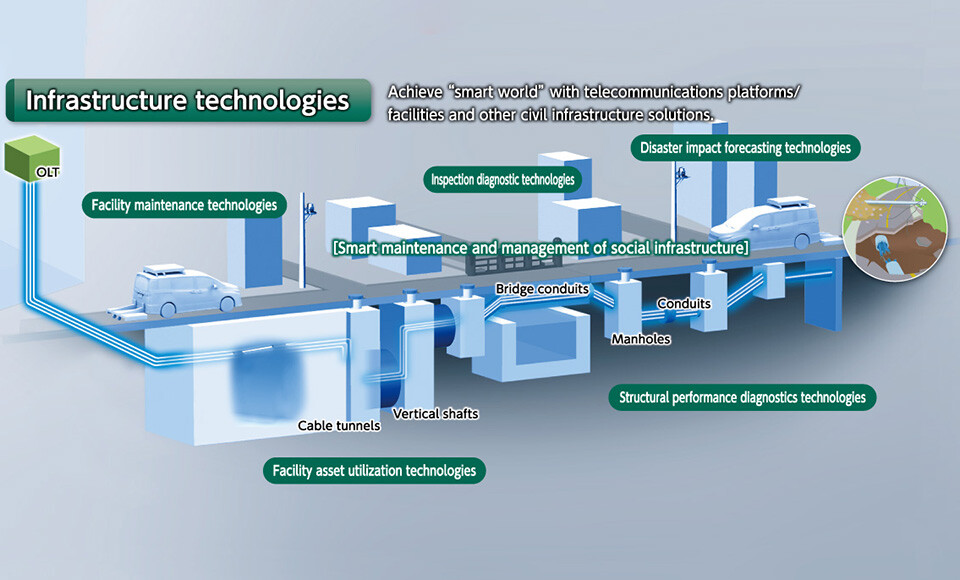
Facility maintenance technologies
The location of buried objects is managed based on their relative position to road alignment (boundaries between road and sidewalk, etc.). If the road alignment changes, for example, due to road widening, the locations of buried objects may become unknown, increasing the risk of damage to NTT facilities from external construction work. As a result, infrastructure-related construction usually requires in-person monitoring of that work, e.g., trial digging, all of which requires much labor.
NTT aims to establish technologies for obtaining location of buried objects through in-conduit sensing, underground radar, and other techniques to make the work of facility management more efficient through the management of absolute 3Dcoordinates of the facility inspection data.
Inspection diagnostic technologies
Due to the ongoing aging of the social infrastructure facilities those support citizen's daily lives and industry and a decreasing number of skilled workers, making the work of inspections and diagnostics more efficient has become an urgent issue. To solve this problem, we aim to establish innovative inspection and diagnostic technology using artificial intelligence (AI) that can support and automate work done by workers recently. This technology will make it possible to inspect various types of facilities in the city including the detection and measurement of cracks, fissures, and corrosion in concrete from digital images of facilities, estimation of the depth of corrosion in steel materials, and assessment of the degree of peeling of road lane markers thereby making work more efficient and optimizing life-cycle cost.
Disaster damage prediction technologies
Since telecommunication services provide an important lifeline which support the citizen's daily lives, and damage on the telecommunication facilities caused by a large-scale disaster will have a massive impact. In particular, given the increasing severity of torrential rains in recent years, a proactive response by estimating the scale of damage based on weather forecasts, etc. is expected to play an important role in maintaining services.
Against this background, we are developing disaster damage prediction technology to evaluate facilities vulnerability and estimate the scale of damage based on past records of damage caused by heavy rains, earthquakes.
Structural performance diagnostics technologies
Many infrastructure facilities are installed beneath roads, meaning that their maintenance and management, such as inspections and repairs, are time-consuming and costly.
It is therefore necessary to determine which types of inspections and repairs can minimize life-cycle costs effectively while ensuring safety for each unit of facilities. For this reason, we are engaged in developing a new technology to optimize inspection timing and to determine the necessity of repair work for individual units of facilities. We work on predicting the state of deterioration (corrosion) of steel used in structures, considering the environments in which these structures are installed and the number of years since installation. Our evaluations also include conducting structural analysis that account for the degree of deterioration.
Facility asset utilization technologies
Environmental problems including climate change have become increasingly severe in recent years, highlighting social problems related to the environment and energy. To solve these problems and achieve a sustainable society, new social infrastructure relating to renewable energy, such as hydrogen transport, power transmission and storage, will be necessary.
We are engaged in the research and development of facility asset usage technology that evaluates the applicability of existing telecommunication facilities to the new facilities. We aim to contribute to these environment activities minimizing construction work and reducing environmental load in the construction of the new social infrastructure.








