IOWN
Here we introduce IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network), an initiative for future communications infrastructure to create a smarter world by using cutting-edge technologies like photonics and computing technologies.
What is Digital Twin Computing?
Overview of IOWN and Digital Twin Computing
"IOWN" (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network) is a communication platform to support the smart world of the near future. NTT is now engaged in research and development with the aim of realizing IOWN by about 2030. As was introduced in the first special feature of this series, "What's IOWN?: Social Background and Purpose", IOWN consists of the following three major technical fields.
- APN: All-Photonics Network
Major improvement to information processing infrastructure potential - DTC: Digital Twin Computing
A new world of services and applications - CF: Cognitive Foundation®
Optimal harmonization of all ICT resources
Here we explain Digital Twin Computing. With Digital Twin Computing we aim to make a "new world of service and applications" based on the all-photonics network that introduces photonics (optics) based technology from every part to the network to terminals and the cognitive foundation that optimally controls all ICT resources. Let's take a look at the image of the world created by Digital Twin Computing.
Creating a digital world for people and society
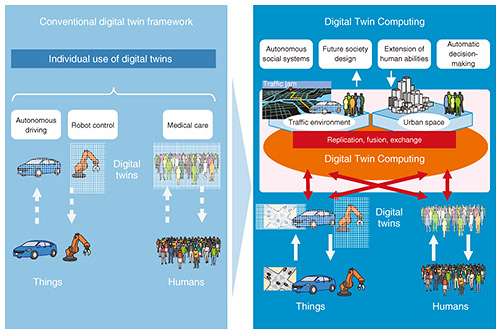
In recent years, the term "digital twin" has entered common use. It means building a twin of a real person or thing in a digital world.
The digital twin framework up to now has been to map individual targets from the real world represented by automobiles, robots, etc. into cyberspace, then analyze those targets and make predictions. The results of such analysis and predictions are then remapped into the real world and put to use.
NTT proposes digital twin computing as an extension of the conventional concept of digital twins. By freely combining and performing calculations on digital twins of objects and humans in diverse industries, we are able to accurately reproduce combinations that could not be comprehensively handled up to now, such as humans and automobiles in cities, and thereby make predictions about the future.
In addition, Digital Twin Computing represents a new computing paradigm that goes beyond physical reproduction of the real world by achieving interactive effects among digital twins including the inner state of humans in cyberspace. This initiative will endeavor to configure a virtual society composed of a variety of digital twins, replicate in cyberspace digital twins of single entities in the real world, and exchange or fuse some of the elements constituting different digital twins to generate new digital twins that do not exist in the real world. This also means that so-called conventional "siloed" digital twins are seamlessly linked rather than having mutual compatibility.
A history of alternately digitalizing humans and things
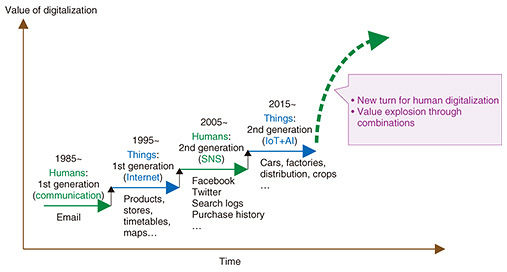
Let's look back at the history of digitalization in relation to humans and things over the past 30 to 40 years. Email appeared around 1985, and was first used for communication. This development can be seen as a step forward in digitalization centered around humans.
Then, around 1995, the Internet appeared, and at the same time, the digitalization of information accelerated in relation to things, which improved daily life and services such as for providing products, timetables, and maps. Next, a new era in human communication appeared around 2005 in the form of social media.
Since 2015, we have been in an era marked by the digitalization of things driven by a combination of Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI). Looking back at this recent history of digitalization, the digitalization of humans and things respectively have been progressing in alternately repeating cycles.
Taking this cycle into account and viewing the recent development of IoT, we believe that it is time for human digitalization to take another turn. Of importance here is that value in this new era will increase not in a linear and proportional manner, but rather in an explosive and discontinuous manner. I predict that the time for this to occur is imminent.
Undertaking to digitally express human consciousness and thoughts
One major feature of Digital Twin Computing is the undertaking to digitally express humans, especially the inner state of individuals. By representing not just the outer state of humans but their inner state as well, it should be possible to achieve advanced interactivity even from a social perspective, such as human mobility and communication.
Moreover, representing the personality of every person should make it possible to achieve interactivity based on diversity and individual features as opposed to interactivity between individual digital twins without personality that are statistically rounded out as average values.
We argue that these features will enable the creation of a virtual society in which a variety of things and humans interact with each other in advanced and sophisticated ways beyond the limitations of the real world.
Two approaches to digital expression of the inner state of humans
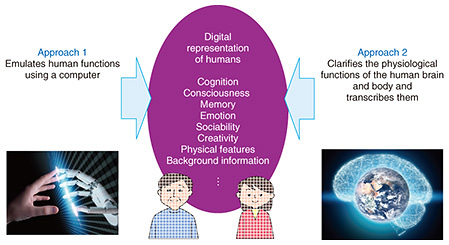
It is important to note that a human digital twin in Digital Twin Computing can provide not only a digital representation of the outer state of humans, but also a digital representation of the inner state of humans, including their consciousness and thoughts.
There are two main approaches to achieving such a difficult objective. The first approach is to emulate human abilities using computers and to repeat that process to "get continuously closer to human qualities". Technologies for recognizing sounds and voices and for communicating via conversation are good examples of how progress can be made with this approach.
The second approach, which might be called the ultimate approach, is to physiologically clarify the human brain and body and transcribe the results to a computer. Much progress has been made in this field, which is representative of neuroscience, and research findings have been produced that can be used for engineering purposes. Our plan is to work toward this digital representation of humans by using the best elements of these two approaches.
Technology getting closer to human qualities
Next we introduce several key technologies that NTT Laboratories have so far taken up with respect to the first approach of "getting closer to human qualities".
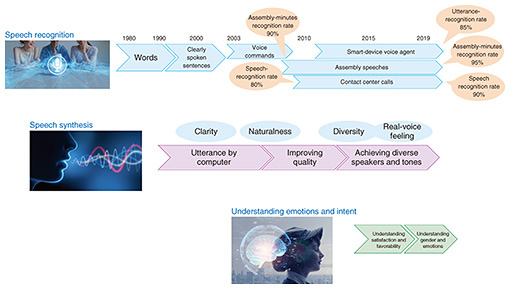
- Speech Recognition
NTT Laboratories have been researching for half a century how to accurately recognize the human voice as a technology for listening. This research began with the recognition of words and clearly spoken sentences, but from around 2010, the technology was able to accurately recognize natural human speech and be used at customer-contact centers. With the introduction of the latest neural networks, the technology is finally approaching the abilities of human speech recognition. - Speech Synthesis
The question here is how and to what extent textual information can be converted to natural, humanlike speech. This technology includes text analysis processing to determine the reading of kanji (Chinese characters) in the Japanese language according to context and processing for synthesizing speech signals with appropriate pitch and speed. Deep learning based on speaker voice data is driving the synthesis of natural and diverse voices that have the feel of a real voice. - Understanding emotions and intent
This technology is capable of detecting cold anger (calm and cool expression of anger), which is usually difficult to infer, from not only the volume and pitch of voices, but also from conversation rhythm, choice of words, etc. It is also able to achieve highly precise recognition of satisfaction, which is a feature that does not appear as easily as dissatisfaction.
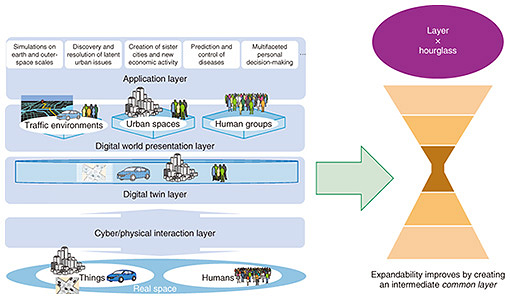
Layered structure and hourglass structure
Of importance when building Digital Twin Computing technology and architecture is whether an hourglass structure can be added to a layered structure as a "common layer".
Like the IP layer on the Internet, the positioning of the IP (Internet protocol) layer as a common layer makes for a smooth interaction between the lower network and upper application layers. This narrow section - this common layer - is necessary and the digital twin layer in Digital Twin Computing architecture will serve as this section.
This digital twin layer maintains digital twins generated from various types of sensor data in real space and derivative digital twins generated from computations on digital twins. These digital twins maintained in the digital twin layer serve as basic constituent elements for constructing diverse virtual societies.
Toward explosion in value through computations on digital twins
Our goal is to make Digital Twin Computing a truly useful concept together with a wide range of interdisciplinary partners including those in social sciences, humanities, etc. We also believe collaboration with a variety of industries is essential to making Digital Twin Computing a reality. Going forward, we plan to cultivate productive partnerships and collect much knowledge to forge a path to a future where the smart world is a reality.
*The content of this article was excerpted and edited from "NTT R&D Forum 2019 Special Sessions: A Digital World of Humans and Society - Digital Twin Computing".
Digital Twin Computing Reference Model is published toward boosting realizing the Digital Twin Computing concept with various partners
NTT published "Digital Twin Computing Reference Model" document which describes mainly the concept and components of the digital twin of things. This is a fist step of materializing "Digital Twin Computing Initiative"(announced on June 10, 2019) with a various collaborative partners.
Click here to download the reference model document.
Serial plan
- #8 Peripheral Technology for the Scalable and Flexible IOWN Network
- #7 Objectives and Overview of Publishing a Reference Document to Realize Our Digital Twin Computing Initiative Together with Our Partners
- #6 IOWN impact on societal infrastructure: MaaS and innovation of energy
- #5 Technology development roadmap for realizing the IOWN concept
- #4 What is the Cognitive Foundation?
- #3 What is Digital Twin Computing?
- #2 What is the All-Photonics Network?
- #1 What's IOWN ? The social background and purpose.